The ESG Imperative in Digital Transformation: Understanding Green Data Centers, Standards, and Certifications

As global enterprises accelerate digital transformation, data centers—at the heart of computing and storage—have become one of the biggest challenges in implementing ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices due to their high energy consumption. To build sustainable IT infrastructure, management must go beyond focusing on performance and consider design from the outset. This article explores how green data centers operate across industries and how organizations can align their facilities with international standards in preparation for green data center certifications.
What Is a Green Data Center? Defining Green Data Centers
Before discussing ESG implementation, it is essential to clarify what a green data center is. Generally, a green data center is one that deliberately prioritizes reducing energy consumption, lowering carbon emissions, and improving resource efficiency throughout design, operation, and maintenance. Compared with traditional data centers that focus primarily on computing performance and stability, green data centers emphasize strict control over environmental impact.
From both international practice and academic perspectives, the scope of green data centers has expanded beyond hardware upgrades to include integrated hardware and software solutions, such as:
- Server virtualization and storage consolidation: Reducing the number of physical devices and improving utilization per machine.
- Equipment replacement strategies: Using more environmentally friendly and durable materials and designs.
- Energy management systems: Implementing precise power monitoring and data analytics.
Green Data Center Standards and Metrics
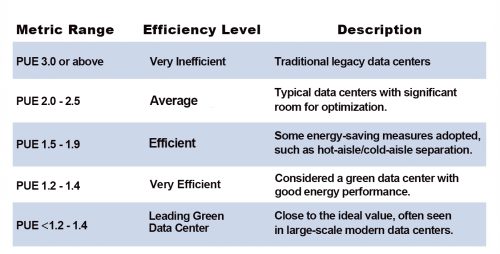
Quantifying the environmental performance of a data center requires a scientific, data-driven approach. Among various green data center standards, one of the most commonly referenced metrics by management and engineering consultants is PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness), proposed by The Green Grid.
PUE measures the ratio of total data center energy consumption to energy consumed by IT equipment. A PUE value closer to 1.0 indicates that a greater proportion of energy is used directly for computing, rather than being consumed by auxiliary systems such as cooling or lighting.
PUE Value Classification:
| Metric | Range | Efficiency Level | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUE | 3.0 or above | Very Inefficient | Traditional legacy data centers, where most energy is consumed by cooling and power losses. |
| PUE | 2.0 - 2.5 | Average | Typical data centers with significant room for optimization. |
| PUE | 1.5 - 1.9 | Efficient | Some energy-saving measures adopted, such as hot-aisle/cold-aisle separation. |
| PUE | 1.2 - 1.4 | Very Efficient | Considered a green data center with good energy performance. |
| PUE | < 1.2 | Leading Green Data Center | Close to the ideal value, often seen in large-scale modern data centers. |
International and Local Accreditation: Common Green Data Center Certification Systems
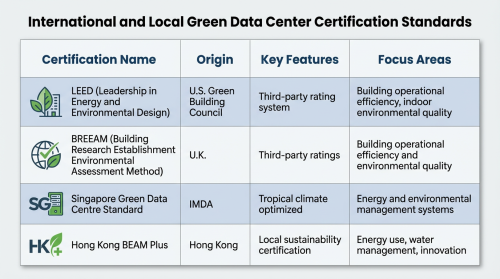
Once enterprises reach the relevant technical benchmarks, the next step is to pursue credible green data center certifications to showcase achievements in market promotion and ESG reporting.
At the international level, widely referenced frameworks include:
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design): Developed by the U.S. Green Building Council, applicable to new or renovated green data center projects.
- BREEAM: Originating in the U.K., provides third-party ratings on building operational efficiency and indoor environmental quality.
At regional and local levels, certifications focused specifically on data centers have also emerged:
- Singapore Green Data Centre Standard: Established by IMDA, designed for data centers in tropical climates, emphasizing energy and environmental management systems similar to ISO 50001.
- Hong Kong BEAM Plus: For data centers in Hong Kong, BEAM Plus certification demonstrates performance in energy use, water management, indoor environmental quality, and innovation, while enhancing a company’s local sustainability profile.
Green Data Center Technical Practices: Airflow Management and High-Efficiency Equipment
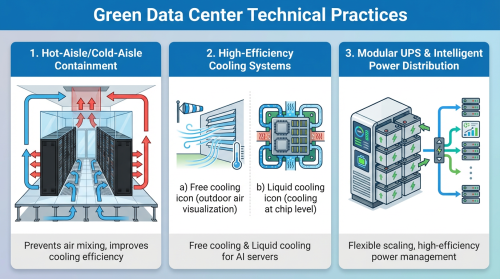
Achieving the above standards requires advanced hardware and technology to implement green data center practices:
1. Hot-Aisle/Cold-Aisle Containment and Airflow Optimization
Traditional data centers often suffer from severe air mixing, reducing cooling efficiency. Green data centers typically employ hot-aisle/cold-aisle containment, physically separating cold supply air from hot exhaust air to prevent short-circuiting of airflow, significantly improving cooling efficiency.
2. High-Efficiency Cooling Systems
Advanced green data centers adopt:
- Free Cooling: Using outdoor air or water sources to reduce compressor runtime.
- Liquid Cooling: Targeted at high-density computing such as AI servers, cooling at the chip level for far higher efficiency than traditional air cooling.
3. Modular UPS and Intelligent Power Distribution
Using modular uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) allows flexible scaling according to actual load, keeping UPS units operating in high-efficiency ranges and minimizing energy conversion losses.
Newtech: Industry-Leading Green Data Center Solution Experts
Newtech has extensive experience in data center engineering and understands the importance of ESG in digital transformation. We provide end-to-end services from consulting, design, and construction to maintenance, helping clients define green data centers and build infrastructure tailored to international green standards and certifications. Our solutions reduce operating costs while delivering on sustainability commitments. Contact us today to begin your journey toward green computing.
References:
ITU & The World Bank – Green Data Centers: Towards a Sustainable Digital Transformation – A Practitioner’s Guide
BEAM Society Limited – Green Data Centres Practice Guide V1.0
Hong Kong Green Building Council – Green Data Centres Practice Guide
BEAM Society Limited – BEAM Plus Data Centres
Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) – Singapore Standard
Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) – Green Data Centre (DC) Roadmap








